Quantitative Modeling
Apply Mathematics to Evaluate Your Financial Assets
|
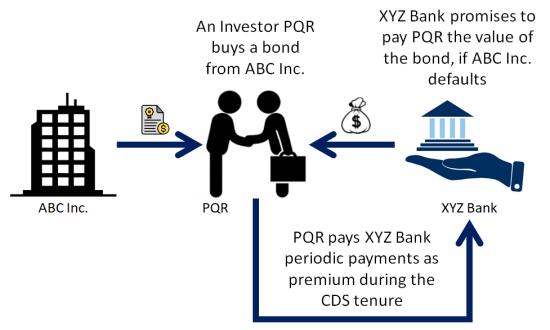
Credit Default SwapThe Credit Default Swap (CDS) provides insurance against the risk of a default by a particular company. The insurer promises to buy a particular corporate bond, issued by the company, at its par value, if the company defaults. As an investor (who has invested in corporate bonds) or a financial institution (who sells the insurance against the default of the company), you will like to price the CDS based on the already available information in the market. Quantitative analysis can help you price the CDS based on the:
|
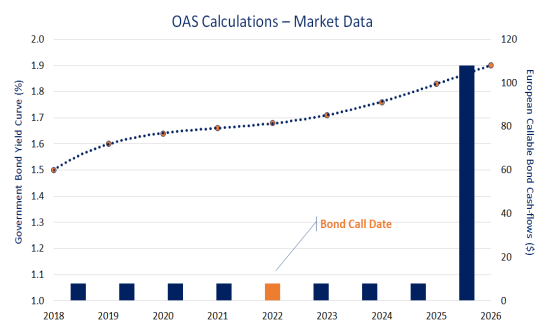
Option Adjusted SpreadOption-Adjusted Spread (OAS) is the constant spread over the government bond rate curve, which takes into account any embedded options in a security. The OAS is calculated such that the security’s cash-flows and optionality, discounted to spot using the OAS rate curve, is equal to the current market price of the security. You, as a trader or a risk manager, may like to know the OAS value. This will help you to value the cost of an embedded option and get an assessment on the general market volatility. You can then know whether the security is worth the given market price or not. Bond Market Association (BMA) has published the BMA ECS Formula, which is widely used to calculate the OAS. |
|
© Copyright 2019 cKlear Analytics